Bureau Events 2017
Bureau Breaks Ground on New Core Research Building

From left to right: Jackson School of Geosciences dean Sharon Mosher, Kenneth Edwards (BEG), Bureau assistant director Jay Kipper, Kim LaValley (BEG), Dr. Robert Loucks (BEG), Bureau director Scott W. Tinker, Mark Blount (BEG), Bureau assistant director Michael Young, Scott Mokry (UT architect and project manager), Chris Zahm (BEG), Bureau assistant director Mark Shuster, Toby Smith (Flintco project manager), and Lauren Alexander (Atkins architect).
On October 5, the Bureau began construction on its new core research building, a project that will provide advanced facilities for scientists conducting research on cuttings and core samples in the Bureau’s Austin Core Research Center.
“Everything we do is built on rocks,” said Bureau director Scott W. Tinker during the groundbreaking ceremony. “It’s exciting to have this new building to show what we’re all about.”
The Bureau, which also acts as the State Geological Survey of Texas, has the largest collection of geologic material in the country in its three core repositories in Austin, Houston, and Midland. The repositories act as a “Library of Congress” for core samples, holding more than 2 million boxes of specimens. These cuttings and core samples are fundamental for research in oil and gas, mineral, and geothermal exploration, as well as in hydrogeology and other fields.
Scientific equipment in the new facility will include a scanning electron microscope on a floating slab, a design that prevents vibrations from traffic on nearby roads from interfering with the delicate instrument. The 10,000-sq-ft building will also include a core viewing room exclusively for use by students and Bureau research staff. The roof of the building will include a terrace for events.

Artist’s rendering of the Bureau’s state-of-the-art core research facilities.
The new building, scheduled for completion by fall 2018, will be located adjacent to the Bureau’s headquarters on The University of Texas at Austin J. J. Pickle Research Campus. After the new construction, the Bureau will begin major renovations on the building that serves as its current core research center, a project that should take 2 to 4 months. The plan is to update 17 labs with state-of-the-art equipment, as well as to update the building’s interior design. In total, the new building and renovations will cost $10 million and are phase one of a larger project, with phase two including the construction of a Texas rock garden between the old and new buildings.
Director Tinker (third from right) joins President Fenves (second from right) and Bureau staff in a horns-up tribute to the University.
Bureau Welcomes UT President Fenves
In September, UT Austin president Gregory L. Fenves, in his first visit to the Bureau, joined Bureau staff at their annual fiscal-year-end gathering.
Bureau director Scott W. Tinker opened the event by thanking President Fenves for his strong support during and following the 2017 session of the Texas Legislature. Although some Bureau programs suffered major cuts in state funding during the session, President Fenves restored millions of dollars to those programs from the University’s overall state appropriations.
Said Fenves, “The Bureau of Economic Geology is unique to the mission of the University. The work that you do has tremendous impact on the state.”
DOE Grants Bureau $4 Million for CCS

Map identifying opportunities for CO2 hub development in southeast Texas incorporating offshore storage.
The U.S. Department of Energy has granted the Bureau $4 million to lead a regional partnership to explore how carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted from industrial facilities along the Gulf Coast can be safely stored in geologic formations under the Gulf of Mexico.
The 4-year program will be led by the Bureau’s Gulf Coast Carbon Center (GCCC) and include institutions and partners from UT Austin and throughout the nation. The goal of fostering safe, long-term storage of CO2, a greenhouse gas that is linked to climate change, involves capturing CO2 from industrial facilities, transporting it offshore, and injecting it into a geologic formation deep beneath the seabed, where it would remain safely stored and isolated from the ocean water.
“This is the type of science that aims at tackling big issues by bringing government, industry, community stakeholders, and academia together to create innovative solutions. It builds on the work our GCCC has been doing the past 15 years in sequestration,” said Bureau director Scott W. Tinker.
The partnership’s mission includes researchers from UT Austin’s Institute for Geophysics (UTIG) and Cockrell School of Engi-neering, U.S. Geological Survey, Louisiana Geological Survey, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Lamar University, and Trimeric Corporation.
GCCC Hosts CO2 Events in Southeast Texas

In June, the Bureau’s Gulf Coast Carbon Center (GCCC) hosted three events in the Beaumont–Port Arthur area to consider both local and global opportunities to capture, transport, and store CO2 in deep geologic formations beneath the Gulf of Mexico.
The second International Workshop on Offshore Geologic CO2 Storage, facilitated by the Bureau’s Katherine Romanak and Tim Dixon from the International Energy Agency Greenhouse Gas (IEAGHG) R&D Programme, was held at the Center for Innovation, Commercialization and Entrepreneurship at Lamar University in Beaumont and featured presentations, posters, and discussion by researchers, project developers, and regulators from China, South Africa, Japan, Norway, France, the Netherlands, the UK, Canada, and across the United States. The Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF) supported travel for several key participants.
Tip Meckel of the Bureau led a field trip highlighting potential CO2 point sources in the Port Arthur industrial corridor, CO2 transportation options, and the highly favorable geology in this region. The thick Miocene sandstones beneath state-owned submerged lands in near-offshore Texas provide a high-quality and exceptionally well-known resource for CO2 storage that has been the topic of Bureau investigations for decades, resulting in significant publications and recent major geologic storage–focused research (Texas Offshore Miocene Project, TXLA Offshore CO2 Storage Resource Assessment, The Search for CO2 Storage). The trip included visits to GT OmniPort and Air Products facilities.
Events concluded with a workshop and open house, hosted by Lamar University, to explore the connections and opportunities between carbon sources and sinks in the Gulf Coast, as part of the CarbonSAFE project. The project, supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, examines the implementation of carbon capture and storage technology in the Golden Triangle Area (Beaumont–Port Arthur–Orange) of southeast Texas.
The information and ideas shared during these events will hopefully lead to international collaboration on offshore CCS projects and, ultimately, stimulate implementation of CCS globally.
CEE Brings Together Energy Leaders
The Center for Energy Economics (CEE) serves a vital role in bringing together energy-thought leaders— educating stakeholders on energy economics and commercial frameworks using comparative research to facilitate energy development. In 2017, the CEE met with various energy regulators to analyze the direction of the group’s ongoing research into the market forces shaping global energy, and it began a collaboration with the Economic Minerals Program to study the underlying market fundamentals that affect minerals and mineral commodities.

Gürcan Gülen
Global Energy Strategy Meetings
In May, the CEE invited stakeholders and supporters of its new member-funded research consortium, the Electric Power Research Forum (EPRF), for a “think day” to analyze and discuss how the EPRF will analyze electricity mar-kets. These complex markets are undergo-ing transformation as utilities and regulatory authorities weigh the impact of a broad spectrum of issues ranging from decreasing government subsidies, distributed generation, electricity storage, and carbon pricing to a reliable power-supply mix that includes renewable sources. One potential research thrust discussed was cost-benefit analyses of various power-delivery options. (For more information about participating in the comprehensive efforts of the EPRF, please contact Gürcan Gülen at gurcan.gulen@beg.utexas.edu.
In June, the CEE hosted its 5th Mid-Year Meeting at its offices in Houston. A diverse group of experts presented information on some of the challenges and opportunities facing global energy industries. Natural-gas markets and related issues were explored in depth, as were retail electricity markets and a relatively new area for CEE research, the economics of mineral resources required in power-generation operations and equipment.
Economic Minerals Program

Sand-resource research leaders Brent Elliott of the Economic Minerals Program and Michelle Foss of the CEE.
Since its founding in 1909, the Bureau has studied the economic viability of the extraction of minerals from Texas. Now, in conjunction with the CEE, the Bureau’s Economic Minerals Program will conduct research and publish its findings on minerals in specific energy-value-chain uses and their supply–demand dynamics. This new collaboration brings the Economic Minerals Program’s expertise in mineral geology and mining engineering together with the CEE’sexpertise in mineral economics and commercial frameworks.
Said Michelle Michot Foss, CEE chief energy economist, “In order to fully evaluate the economics and viability of both conventional and alternative energy systems, it is vital that we understand the resource endowments and value-chain/supply-chain economics of critical minerals.”
Some of the key minerals being studied now include hydraulic-fracturing sand, lithium, cobalt, graphite, rare earth elements, metallic ores, uranium, and aggregate resources. Areas of research will include geologic mapping, resource estimation, extraction and processing technology, commercial frameworks, value chains, international trade, extraction economics and industrial organization, and commercialization.
For more information on how you can be involved in this collaboration between CEE and the Economic Minerals Program, please contact Brent Elliott.
A Closer Look at Sand Resources

Above: A quarry in the Hickory Sandstone of the Riley Formation. (Photo by Rich Kyle; location courtesy of Proppant Specialists). Inset: Rounded, relatively uniform grains like these from the Kermit sand are desirable for applications like fracking.
One economically significant application of mineral resources studied by the CEE and Economic Minerals Program is the sand (proppant) used in fracking wells in the oil and gas industry. Fracking operations have seen a steady rise in the amount of sand used in each well, almost doubling in volume over the last 5 years. The United States produced 95 million metric tons of industrial sand in 2015, more than half of the global sand production; 71% of the U.S. tonnage was used as hydraulic fracturing sand and well-packing and cementing sand.
The Bureau is engaged in geologic mapping of sand resources, especially formations and units like the Hickory Sandstone of the Riley Formation that produce much of the traditional frac sand from Central Texas. Part of a sand-resource analysis includes the use of geospatial modeling techniques to map out the most favorable areas for exploration and resource extraction. Researchers determine where the sand is being transported, what kind of transportation infrastructure and possible pathways for transport (such as trucks or trains) exist, distances of quarry operations to metropolitan areas that may require more resources as population grows, and other characteristics like resource quality and stripping ratio to build a combined map of new favorable sand-mining sites across Texas.
Because transportation costs make up a majority of the expense in distributing sand for quarry operations to consumer site locations, the Bureau also creates transportation models that integrate costs, distances, routing, trans-loading, and other important factors to generate network datasets for all modes of transportation infrastructure in Texas. These models allow researchers to identify new infrastructure development opportunities and predict the impact of new transport infrastructure like railroads, highways, and freight-transfer stations near mining sites and hydraulic fracturing sites.
With sand resources playing a significant role in the extraction of hydrocarbons from the prolific shale and tight oil formations of Texas and elsewhere in the U.S., sand research by the Bureau of Economic Geology will play an integral role in influencing the decisions of the American energy industry for many years to come.
Ikonnikova Presents Energy Webinar

Svetlana Ikonnikova
In July, Bureau research scientist and energy economist Svetlana Ikonnikova presented the webinar “Energy Forecasting: Shale Gas” with energy analyst John Staub of the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Webcast by the AIChE Academy, the 1-hr talk covered key topics—especially the roles of technology, geology, and uncertainty in efforts to accurately forecast future shale production—that are central to Ikonnikova’s ongoing research as part of the Bureau’s comprehensive Shale Production and Reserves Study. Ikonnikova serves as co-PI of the program, among the most extensive integrated studies of shale production and economics in the United States to date, and has authored or co-authored numerous papers resulting from that research. The Bureau program recently concluded a comprehensive study of the Bakken unconventional resource in North Dakota and Montana and reported summaries of its findings at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in Austin in July.
The “Energy Forecasting: Shale Gas” webinar can be viewed at the AlChe Academy site, which provides a wide range of educational resources for topics such as energy, chemical and biological engineering, and sustainability and environment.
STARR Hosts Core Workshop

William Ambrose (left) explains core samples to work-shop attendees.
In October, the State of Texas Advanced Resource Recovery (STARR) program hosted a core workshop, “Shelf-to-Basin Architecture, Depositional Systems, and Facies Variability of the Southern Eastern Shelf of the Permian Basin,” featuring presentations by Tucker F. Hentz, William A. Ambrose, Robert W. Baumgardner, and Fritz Palacios. The event, sponsored by the Austin Geological Society, offered an in-depth overview of shelf, shelf-edge, and slope-depositional-facies characteristics; stratigraphic variations; and sedimentation trends across the southern Eastern Shelf and adjacent Midland Basin, a region that is currently the site of both conventional and unconventional exploration and production. For more information on the region, see the Bureau’s Report of Investigations 282.
The STARR program conducts geologic research that increases the production and profitability of oil and gas wells in the State of Texas. Since its inception in 1996, STARR has helped raise $515.6 million in severance tax revenues, offsetting the program’s $39.8 million funding investment, and has undertaken more than 60 field (reservoir characterization) and 15 regional studies. Over 50 Texas oil and gas operators participate in the program. Results of STARR regional studies are used by oil companies as the basic framework for their exploration efforts. Core workshops such as this one are a key component in the technology transfer process. To learn more about STARR and future workshops, please contact William Ambrose at william.ambrose@beg.utexas.edu.
18th Annual Austin Earth Science Week Career Day
In October, the Bureau joined with area geoscience professionals to host the 18th Annual Austin Earth Science Week Career Day, which engages students in discovering earth sciences, encourages Earth stewardship, and motivates geoscientists to share their knowledge of and enthusiasm for our planet. Participants included 340 middle school students from Bastrop, Gorzycki, Ridgeview, and Bedicheck middle schools, joined by the Eco-Explorers and Austin Area Homeschool Science Team.
Students participated in presentations, demonstrations, and hands-on activities showcasing exploration geology, hydrology, seismology, geophysics, paleontology, geologic mapping, meteorology, planetary and solar system studies, gems and minerals, archeology, and engineering. The events were led by approximately 65 geoscience professionals from the U.S. Geological Survey, Texas Water Development Board, City of Austin, TxDOT, Lower Colorado River Authority, KOKE FM radio, Texas Commission on Environment-al Quality, and others. Financial sponsors included Statoil (underwriting sponsor), Austin Geological Society, Parsley Energy, Schlumberger, and The Subsurface Library of Midland.

Left: John Hash of the GeoFORCE program leads students though the Great Global Race activity. Center: Leyon Greene of the Texas Water Development Board demonstrates aspects of the TexMesonet program to students. Right:Statoil volunteer Codie Kretzer shows a middle-school student how to use a hand lens to examine a 3-billion-year-old rock.

Dr. Ali Goudarzi explains his poster
5th Annual Bureau Research Symposium
In September, Bureau research scientists, postdoctoral researchers, graduate students, and support staff gathered for the 5th Annual Bureau Research Symposium, whose goal is to promote project collaborations and the interchange of ideas between researchers.
This year, the event showcased not only 32 posters illustrating research efforts but also a new format suggested by staff: short oral presentations, or “nanotalks.” Staff voted on their favorite poster and nanotalk presentations: the nanotalk “Deepwater Channel Trajectory Controls on Reservoir Connectivity” by Ph.D. candidate Paul Morris, and the poster “Topographic Control on the Subsurface Heat Budget of Ice Wedge Polygons” by Ph.D. candidate Chuck Abolt and Associate Director Michael Young.
Industry Day 2017

Houston Research Center
In March, the Bureau hosted Industry Day 2017 at its Houston Research Center, where over 90 representatives from companies large and small attended the seminar featuring topics of current interest presented by the Bureau’s top researchers.
Among the presentations were updates on the progress of the Bureau’s renowned shale studies, including the Tight Oil Resource Assessment (TORA) project, its newest undertaking to understand the complex oil-producing formations of the Permian Basin. Also featured were a presentation on Bureau research into a novel tool to improve seismic imaging; a progress report on the status of the TexNet earthquake-monitoring network and its research arm, the Center for Integrated Seismicity Research (CISR); and a lunchtime overview of research related to water issues in shale-formation production.
Bureau director Scott W. Tinker welcomed Industry Day guests with an overview of the Bureau’s major initiatives, stressing the vital importance and practicality of industry partnerships and of industry support for joint research projects.
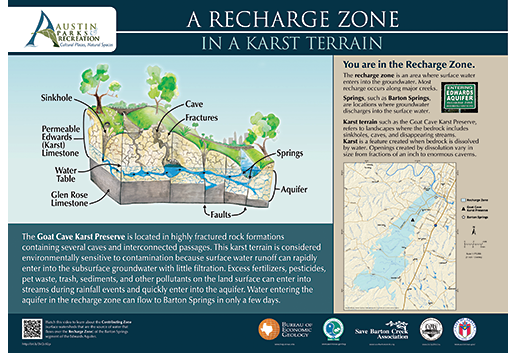
This Goat Cave Karst Preserve GeoSign is an example of interpretive signs teaching about the geology and environment of selected sites around Texas.
Bureau Unveils New Texas GeoSigns
In April, Bureau information geologist Linda Ruiz McCall spoke to attendees at the unveiling of five new interpretive signs at the Goat Cave Karst Preserve in South Austin. The signs installed at the site encourage good stewardship of the land and explain the karst terrain, endangered species, and interaction between surface water and groundwater in the recharge zone of the Edwards Aquifer system. Project partners include the City of Austin, the Balcones Canyonlands Preserve, the Save Barton Creek Association, the Austin Parks Foundation, and many citizen volunteers.
The Goat Cave Karst Preserve signs are part of the broader Texas GeoSign Project, whose goal is to promote the understanding of geologic information. McCall leads the project, which includes Bureau team members Chock Woodruff, Cari Breton, Jamie Coggin, Cathy Brown, Amanda Masterson, and Jay Kipper. If you are interested in learning more about this initiative, please contact Linda McCall.
Educational Workshops and Training

Children at the 2017 Boy Scout STEMboree examine and identify rocks and minerals.
In 2017, Bureau research and support staff reached over 1,500 Texas K–16 educators and students, as well as members of community groups, with educational workshops, presentations, training, and field experiences focusing on the geology of the state and on the innovative research of the Bureau.
Outreach to K–12 teachers included training on the Balcones Fault Zone Aquifer, Texas industrial minerals, geologic maps and satellite imagery, and rocks and minerals. Educators were also informed about EarthDate, the Bureau’s new public radio series, and Texas Through Time, the Bureau’s recently released book about the geology of the state.

Palacios High School advanced physics students collect beach-profile data from site MAT02 on Matagorda Peninsula.
Outreach to K–12 students focused on careers in geoscience, rocks and minerals, earth processes, and research at the Bureau. Students from the GeoFORCE 12th-grade Summer Academy were given presentations and tours of the Austin Core Repository. Bureau geoscientists Jeff Paine, Tiffany Caudle, Peter Flaig, and Linda Ruiz McCall also served as instructors for the GeoForce Summer Academy programs. In addition to in-person presentations, the Bureau’s distance-learning outreach offered 150 5th-grade students from Austin Elementary School in Irving, Texas, a virtual field trip via the internet from Enchanted Rock to the Texas coast to learn about weathering and erosion.
The Texas High School Coastal Monitoring Program (THSCMP), which is led by Tiffany Caudle, marked its 20th anniversary in 2017. The THSCMP is a research and outreach project that engages students and teachers who live along the Gulf of Mexico in the study of their natural environment. Students collect data in a real-world setting that are used by working scientists to address coastal issues. A total of 294 data-collection field trips have been completed through this program to date.

Bureau associate director Michael Young shows core samples to members of the Austin Regional Sierra Club.
In undergraduate outreach, students from San Angelo State University toured the Austin Core Repository and listened to presentations from Bureau research and support staff including Bill Ambrose, Tucker Hentz, Brent Elliott, Robert Baumgardner, Nathan Ivicic, and Linda Ruiz McCall. Texas Association of Community College geology professors learned how they might use Texas Through Time in courses they teach.
In community outreach, the Bureau hosted the Austin Regional Sierra Club for presentations about environmental research. Michael Young, Sue Hovorka, Bridget Scanlon, Brad Wolaver, Daniel Ortuño, and Linda Ruiz McCall each spoke, and the group also toured the Austin Core Repository with Nathan Ivicic and Brandon Williamson. Presentations were also given to the Austin Gem and Mineral Society and the 2017 Boy Scout STEMboree.
Conference for the Advancement of Science Teaching

Juli Hennings (left) and Linda Ruiz McCall

Jason Barrett of TxDot and Beverly DeJarnett of the Bureau distribute maps, rock kits, and posters at the Bureau exhibit booth at CAST.
Bureau project manager Juli Hennings and information geologist Linda Ruiz McCall presented information on the Bureau’s new radio program EarthDate to K–12 educators at the Conference for the Advancement of Science Teaching (CAST) in Houston in November. Hosted by the Science Teachers Association of Texas, CAST draws over 5,500 science educators from across the state to provide professional development and resources to advance K–12 science education in Texas.
Research Scientist Associate Beverly DeJarnett of the Bureau and Jason Barrett of the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDot) also distributed hundreds of rock and mineral posters, rock kits, maps, and informational brochures in the CAST Exhibit Hall. American Geosciences Institute Earth Science Week Toolkits, rock kits, and hundreds of page-sized maps were also donated to the Texas Earth Science Teachers Association for distribution to their members statewide.
For additional information about the K–12 educational and outreach resources offered by the Bureau, please contact Linda McCall.