|
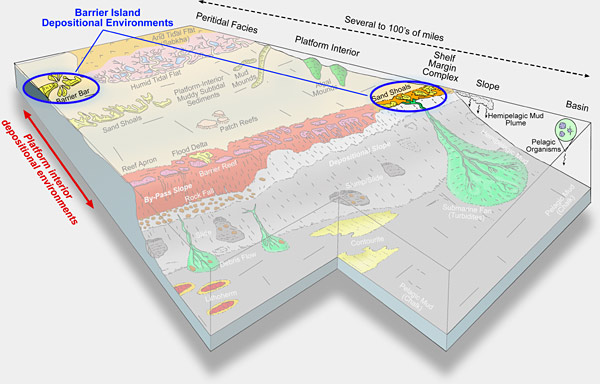
The barrier-island
system can be divided into several environments:
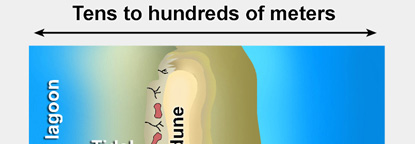
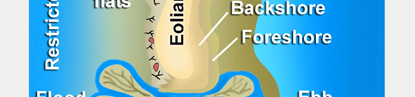
(1) Beach: Includes sediments from the
shoreface, foreshore, and backbeach.
(2) Eolian dune: Well-developed eolian
sand dunes commonly form landward of the backbeach.
(3)
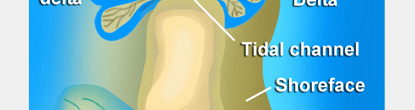
Tidal-channel facies: Tidal channels commonly dissect
barrier islands. Channels can contain mud-free to muddy
sand depending on their depth, tidal current energy, and
density of sea-grass growth.
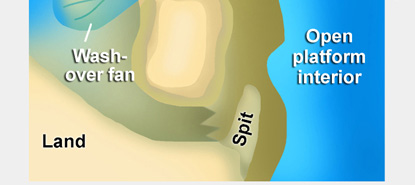
(4)
Sand spit facies: Sand spits can accrete laterally
into tidal channels in barrier-island complex.
(5)
Flood-delta facies: As tides and storms force water
through tidal channels, deltas form on the flood end of
the channel. These deposits range from sandy facies with
isolated corals and red algae to a muddy facies with sea
grass.
(6) Ebb-delta facies: As tides and storm
waters drain back out through tidal channels, deltas form
on the ebb end of the channel and produce sandy facies with
corals and red algae.
|